Turning off all 7 of these features will make Windows 11 feel much less intrusive (and some might boost your computer’s performance), and you’ll have a more enjoyable user experience. Say goodbye to annoying notifications disrupting your workflow, targeted ads, data collection, and more.
1. Pop-up banner notifications
In Windows 11, you’ll often see banner notifications appear in the bottom right corner of your screen. These notifications might contain important system alerts or a not-so-important article from a website you allowed notifications for, but they’re generally regarded as a bit annoying.
If you’ve ever found these pop-up banner notifications distracting, here’s how to disable them.
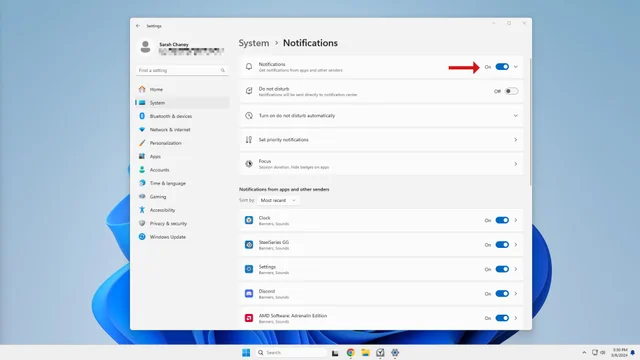
1. Open the Settings app.
2. Click on System in the left menu.
3. Select Notifications from the center menu.
4. Toggle off the switch next to Notifications at the top of the window.
If you only want to disable notifications temporarily, you can toggle on Do Not Disturb and set up custom times to not receive notifications.
2. Start menu notifications and recommendations
If you’re not using OneDrive or your Microsoft user account is missing info, you’ll see account-related notifications in the Start menu. Here’s how to stop seeing these pesky notifications.
1. From your Settings app, select Personalization from the left menu.
2. Click on Start in the center menu.
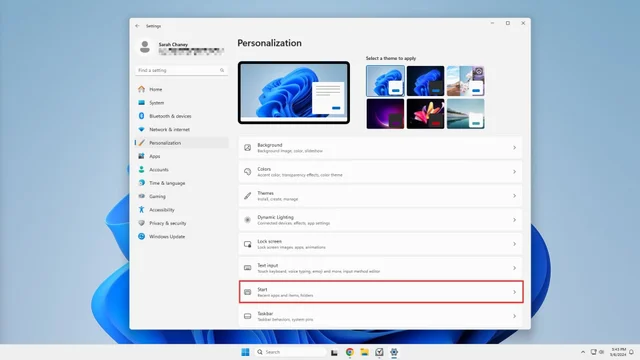
3. Toggle off the switch next to Show account related notifications occasionally in Start.
The Start menu is also home to recommendations, which can sometimes be helpful, but are more often just a nuisance. To turn these off, toggle the switch next to Show recommendations for tips, shortcuts, new apps, and more.
3. Targeted Microsoft ads
With ads on almost every website you visit and in your social media feed, it’s no surprise that Windows 11 tracks your activities so advertisers can send personalized ads your way. While you unfortunately can’t turn off ads completely on Windows 11, you can disable the use of your unique advertising ID to stop seeing targeted ads.
1. Head to your Settings app.
2. Click on Privacy & Security in the left menu.
3. Select General from the center menu
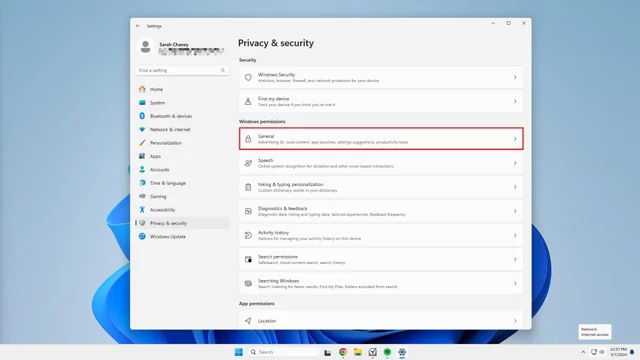
4. Next to Let apps show me personalized ads by using my advertising ID, toggle the switch off.
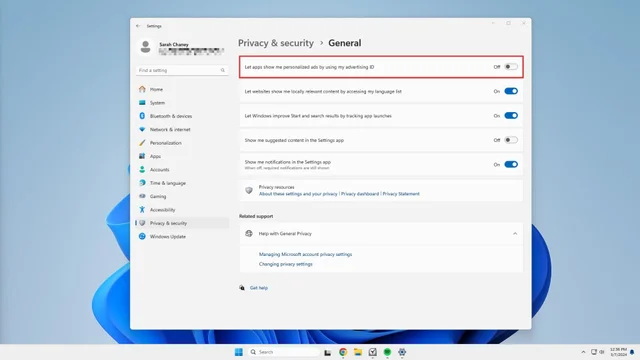
Optionally, while you’re here, you can also toggle off the switches next to Let Windows improve Start and search results by tracking app launches and Show me notifications in the Settings app.
4. News feed from Widgets
Widgets are one of the best Windows 11 features because they give you a quick glance at info from the apps you’ve added, but the news feed added by default is unnecessary.
1. Open your Widgets board by pressing the Windows key followed by the W key.
2. Click the Settings button (cog gear icon) in the top right corner of the Widgets board.
3. Select Show or hide feeds from the menu.
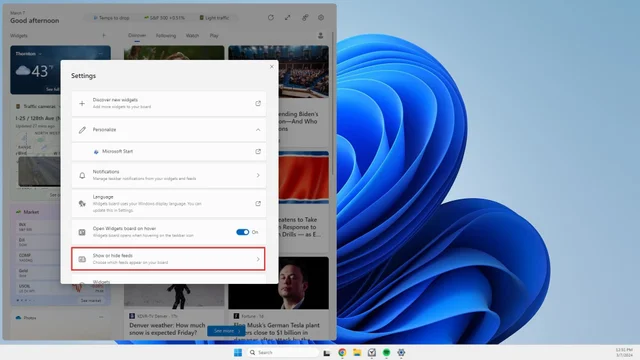
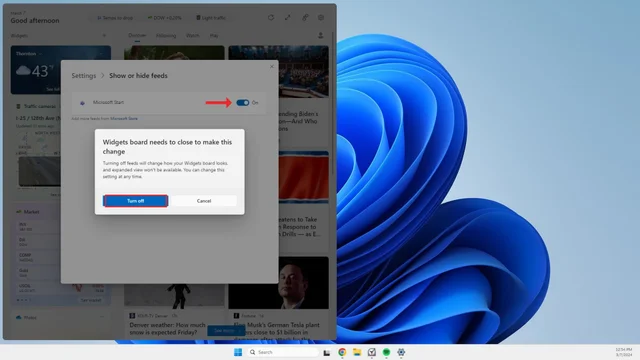
4. Toggle off the switch next to Microsoft Start.
5. A pop-up window will appear to confirm your decision. Select Turn off, and when you open your Widgets board next, the news feed will be gone.
5. Optional diagnostic data and feedback
In order to improve the Windows 11 experience, Microsoft collects a lot of data about your computer and how you use it. While real user experience can certainly help Microsoft improve its operating system, it’s not necessary. Here’s how to limit the amount of diagnostic data and feedback your computer sends to Microsoft.
1. Open your Settings app.
2. Select Privacy & security from the left menu.
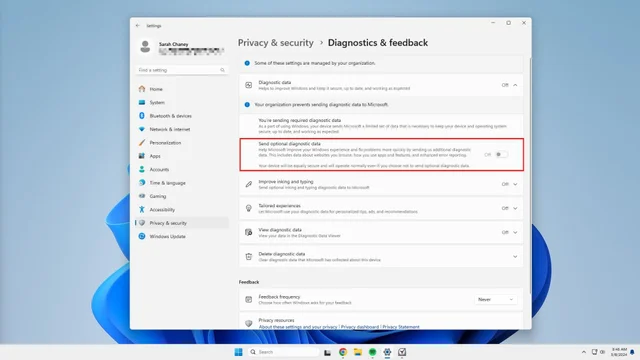
3. Click Diagnostics & feedback in the center menu.
4. Toggle off the switch next to Send optional diagnostic data.
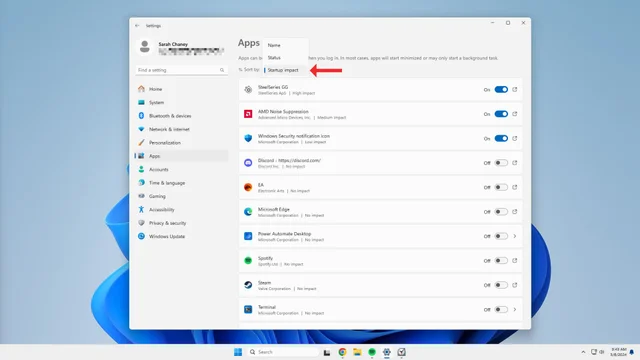
6. Unnecessary startup apps
Many applications open during startup by default, and this can majorly slow down your computer’s overall performance, especially if you don’t notice certain apps are open. If you’re not using an app, there’s no reason for it to be open and sucking up system resources.
Seeing which apps are set to launch at startup and turning them off is incredibly simple to do.
1. Open your Settings app.
2. Select Apps from the left menu.
3. Click on Startup at the bottom of the center menu.
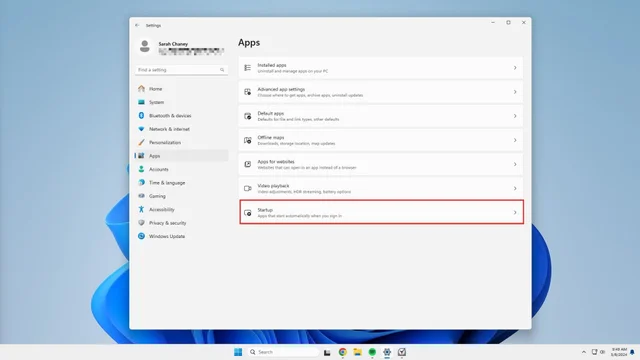
4. At the top of the window, there’s a Sort by dropdown menu. From the available options, select Startup impact to see which apps are demanding the most resources from your computer.
5. Toggle off any apps you don’t need to open during startup.
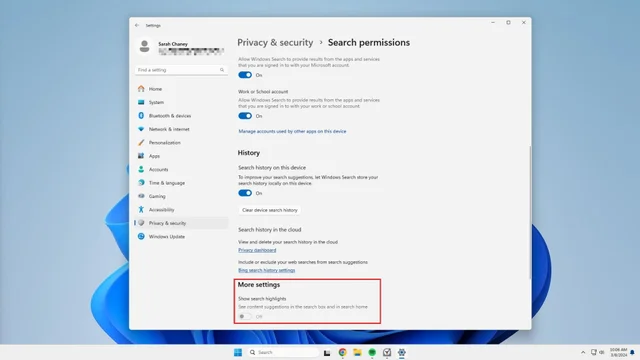
7. Search highlights from Bing
Microsoft’s proprietary search engine is Bing, so you’ll see Bing search highlights when using the the Windows 11 Search interface. If you don’t want to see these Bing results every time you search for something, you can turn this feature off in four simple steps.
1. Open your computer’s Settings app.
2. Click on Privacy & security in the left menu.
3. Select Search permissions towards the bottom of the center menu.
4. Scroll down to the More settings heading, and toggle off the switch for Show search highlights.
While most of the features just mentioned are objectively annoying, there’s one new feature in Windows 11 that could be seen by some as helpful and by others as intrusive: Microsoft’s new AI Copilot tool. Copilot can help you write emails or summarize long walls of text, but it’s quite a resource-heavy app.
If you don’t want Microsoft’s new AI digital assistant on your device, here’s how to turn off Copilot on Windows 11.
